XDMoD Tool
XDMoD Overview
XDMoD, which stands for XD Metrics on Demand, is an NSF-funded open source tool that provides a wide range of metrics pertaining to resource utilization and performance of high-performance computing (HPC) resources, and the impact these resources have in terms of scholarship and research.
How to log in
Visit OSC's XDMoD (xdmod.osc.edu) and click 'Sign In' in the upper left corner of the page.

XDMoD Tabs
When you first log in you will be directed to the Summary tab. The different XDMoD tabs are located near the top of the page. You will be able to change tabs simply by click on the one you would like to view. By default, you will see the data from the previous month, but you can change the start and end date and then click 'refresh' to update the timeframe being reported.
Summary:
The Summary tab is comprised of a duration selector toolbar, a summary information bar, followed by a select set of charts representative of the usage. The Summary tab provides a dashboard that presents summary statistics and selected charts that are useful to the role of the current user. More information can be found at the XDMoD User Manual.
Usage:
The Usage tab is comprised of a chart selection tree on the left, and a chart viewer to the right of the page. The usage tab provides a convenient way to browse all the realms present in XDMoD. More information can be found at the XDMoD User Manual.
Metric Explorer:
The Metric Explorer allows one to create complex plots containing multiple multiple metrics. It has many points and click features that allow the user to easily add, filter, and modify the data and the format in which it is presented. More information can be found at the XDMoD User Manual.
App Kernels:
The Application Kernels tab consists of three sub-tabs, and each has a specific goal in order to make viewing application kernels simple and intuitive. The three sub-tabs consist of the Application Kernels Viewer, Application Kernels Explorer, and the Reports subsidiary tabs. More information can be found at the XDMoD User Manual.
Report Generator:
This tab will allow you to manage reports. The left region provides a listing of any reports you have created. The right region displays any charts you have chosen to make available for building a report. More information can be found at the XDMoD User Manual.
Job Viewer:
The Job Viewer tab displays information about individual HPC jobs and includes a search interface that allows jobs to be selected based on a wide range of filters. This tab also contains the SUPReMM module. More information on the SUPReMM module can be found below in this documentation. More information can be found at the XDMoD User Manual.
About:
This tab will display information about XDMoD.
Different Roles
XDMoD utilizes roles to restrict access to data and elements of the user interface such as tabs. OSC client holds the 'User Role' by default after you log into OSC XDMoD using your OSC credentials. With 'User Role', users are able to view all data available to their personal utilization information. They are also able to view information regarding their allocations, quality of service data via the Application Kernel Explorer, and generate custom reports. We also support the 'Principal Investigator' role, who has access to all data available to a user, as well as detailed information for any users included on their allocations or project.
References, Resources, and Documentation
Job Viewer
The Job Viewer Tab displays information about individual HPC jobs and includes a search interface that allows jobs to be selected based on a wide range of filters:
1. Click on the Job Viewer tab near the top of the page.
2. Click Search in the top left-hand corner of the page
3. If you know the Resource and Job Number, use the quick search lookup form discussed in 4a. If you would like more options, use the advanced search discussed in 4b.
4a. For a quick job lookup, select the resource and enter the job number and click 'Search'.
4b. Within the Advanced Search form, select a timeframe and Add one or more filters. Click to run the search on the server.
5. Select one or more Jobs. Provide the 'Search Name', and click 'Save Results' at the bottom of this window to view data about the selected jobs.
6. To view data in more details for the selected job, under the Search History, click on the Tree and select a Job.
7. More information can be found in the section of 'Job Viewer' of the XDMoD User Manual.
XDMoD - Checking Job Efficiency
Intro
XDMoD can be used to look at the performance of past jobs. This tutorial will explain how to retreive this job performance data and how to use this data to best utilize OSC resources.
First, log into XDMoD.
You will be sent to the Summary Tab in XDMoD:
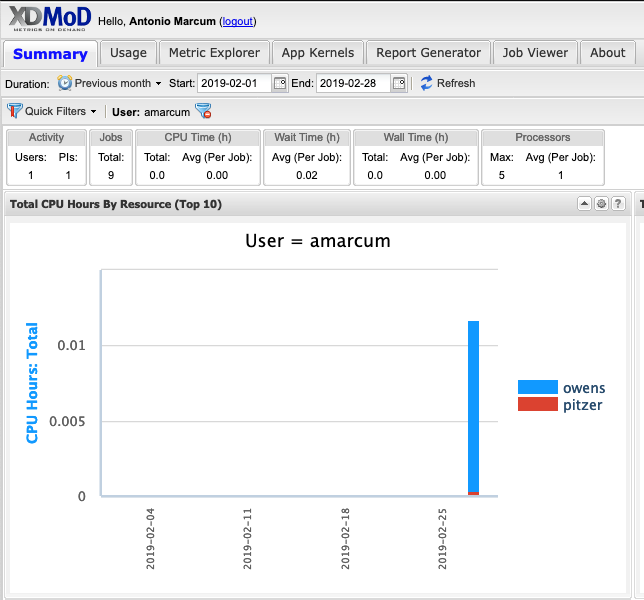
Click on the Metric Explorer tab, then navigate to the Metric Catalog click SUPREMM to show the various metric options, then Click the "Avg CPU %: User: weighted by core hour " metric.
A drop-down menu will appear for grouping the data to viewed. Group by "CPU User Value
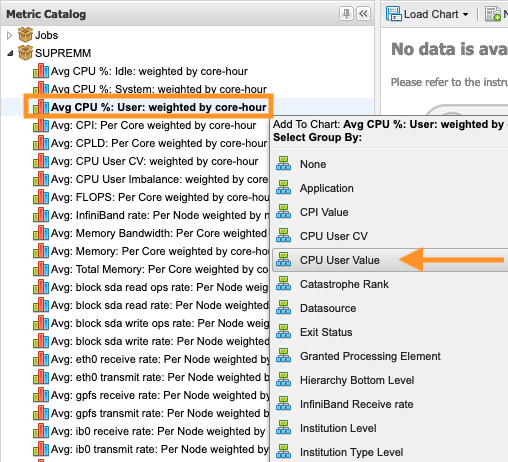 ":
":
This will provide a time-series chart showing the average 'CPU user % weighted by core hours, over all jobs that were executing' separated by groups of 10 for that 'CPU User value'.
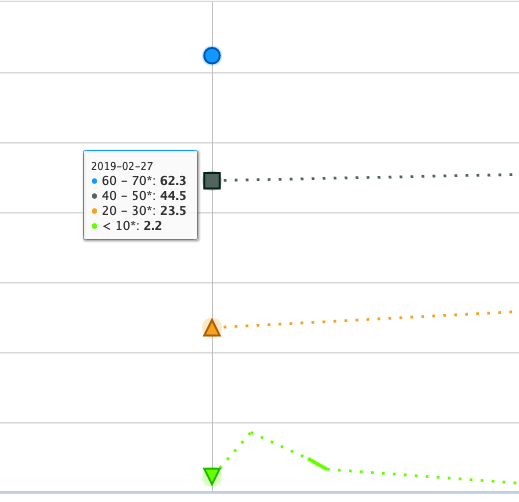
One can change the time period by adjusting the preset duration value or entering dates in the "start" and "end" boxes by selecting the calendar or manually entering dates in the format 'yyyy-mm-dd'. Once the desired time period is entered the "Refresh" button will be highlighted yellow, click the "Refresh" button to reload that time period data into the chart.

Once the data is loaded, click on one of the data points, then navigate to "Drilldown" and select "Job Wall Time". This will group the job data by the amount of wall time used.
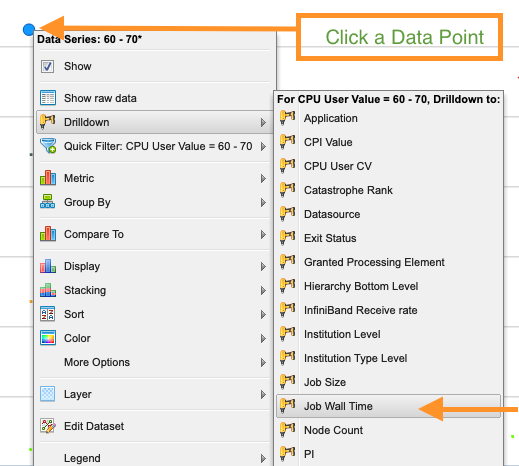
Generally, the lower the CPU User Value, the less efficient that job was. This chart can now be used to go into some detailed information on specific jobs. Click one of the points again and select "Show raw data".
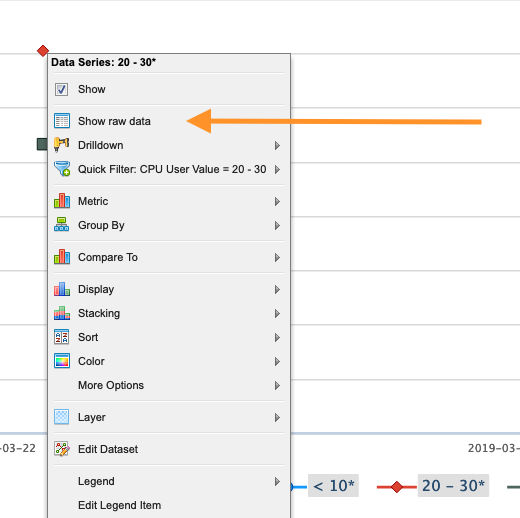
This will bring up a list of jobs included in that data point. Click one of the jobs shown.
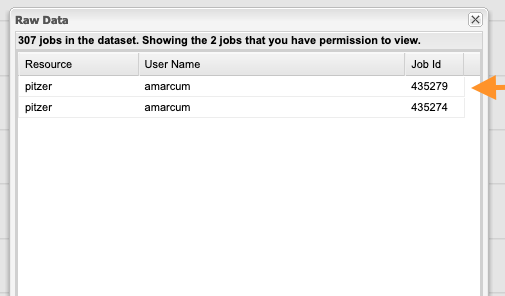
After loading, this brings up the "Job Viewer" Tab for showing the details about the job selected.

It is important to explain some information about the values immediately visible such as the "CPU User", "CPU User Balance" and "Memory Headroom".
The "CPU User" section gives a ratio for the amount of CPU time used by the job during the time that job was executing, think of it as how much "work" the CPUs were doing doing execution.
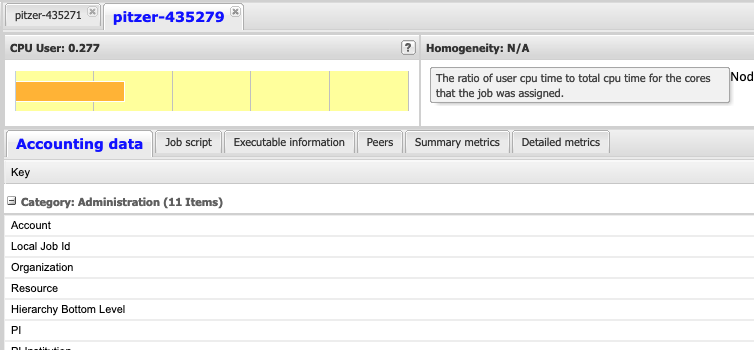
The "CPU User Balance" section gives a measure for how evenly spread the "work" was between all the CPUs that were allocated to this job while it was executing. (Work here means how well was the CPU utilized, and it is preferred that the CPUs be close to fully utilized during job execution.)
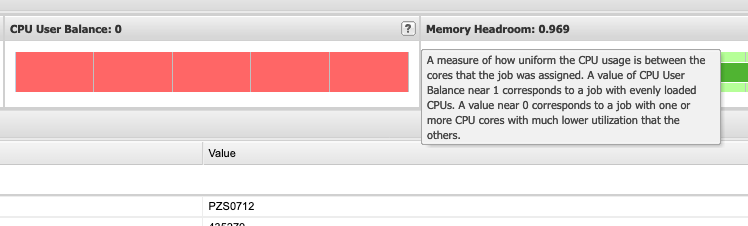
Finally, "Memory Headroom" gives a measure for the amount of memory used for that job. It can be difficult to understand what a good value is here. Generally, it is recommended to not specifically request an amount of memory unless the job requires it. When making those memory requests, it can be beneficial to investigate the amount of memory that is actually used by the job and plan accordingly. Below, a value closer to 0 means a job used most of the memory allocated to it and a value closer to 1 means that the job used less memory than the job was allocated.
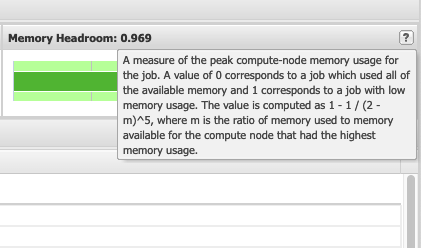
This information is useful for better utilizing OSC resources by having better estimates of the resources that jobs may require.