R is a language and environment for statistical computing and graphics. It is an integrated suite of software facilities for data manipulation, calculation, and graphical display. It includes
- an effective data handling and storage facility,
- a suite of operators for calculations on arrays, in particular matrices,
- a large, coherent, integrated collection of intermediate tools for data analysis,
- graphical facilities for data analysis and display either on-screen or on hardcopy, and
- a well-developed, simple and effective programming language which includes conditionals, loops, user-defined recursive functions and input, and output facilities
More information can be found here.
Versions
The following versions of R are available on OSC systems:
| Version |
Pitzer |
Ascend |
Cardinal |
| 4.4.0 |
X |
X |
X* |
R/4.4.0 l is compiled with gcc/12.3.0. To load R/4.4.0, please load the gcc/12.3.0 module first.
* Current default version
** The user state directory (session data) is stored at ~/.local/share/rstudio for the latest RStudio that we have deployed with R/4.1.0. It is located at ~/.rstudio for older versions. Users would need to delete session data from ~/.local/share/rstudio for R/4.1.0 and ~/.rstudio for older versions to clear workspace history.
Known Issue
There's a known issue loading modules in RStudio's environment after changing versions or clusters.
If you have issues using modules in the RConsole - try these remedies
- restarting the terminal
- restarting the RConole
- logging out of the RStudio session and logging back in.
- remove your ~/.local/share/rstudio
You can use module avail R to view available modules and module spider R/version to show how to load the module for a given machine. Feel free to contact OSC Help if you need other versions for your work.
Access
R is available to all OSC users. If you have any questions, please contact OSC Help.
Publisher/Vendor/Repository and License Type
R Foundation, Open source
R software can be launched two different ways; through Rstudio on OSC OnDemand and through the terminal.
In order to access Rstudio and OSC R workshop materials, please visit here.
In order to configure your environment for R, please run the following command:
module load gcc/version R/version
#for example,
module load gcc/12.3.0 R/4.4.0
R/4.4.0 and onwards versions use gcc compiler. Loading R/4.4.0 requires the dependency gcc/12.3.0 to also be loaded.
Using R
Once your environment is configured, R can be started simply by entering the following command:
R
For a listing of command line options, run:
R --help
Running R interactively on a login node for extended computations is not recommended and may violate OSC usage policy. Users can either request compute nodes to run R interactively or run R in batch.
Running R interactively on terminal:
Request compute node or nodes if running parallel R as,
sinteractive -A <project-account> -N 1 -n 28 -t 01:00:00
When the compute node is ready, launch R by loading modules
module load gcc/12.3.0 R/4.4.0
R
Reference the example batch script below. This script requests one full node on the Cardinal cluster for 1 hour of wall time.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --job-name R_ExampleJob
#SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=48
#SBATCH --time=01:00:00
#SBATCH --account <your_project_id>
module load gcc/12.3.0
module load R/4.4.0
cp in.dat test.R $TMPDIR
cd $TMPDIR
R CMD BATCH test.R test.Rout
cp test.Rout $SLURM_SUBMIT_DIR
R comes with a single library $R_HOME/library which contains the standard and recommended packages. This is usually in a system location.
Users can check the library path as follows after launching an R session;
> .libPaths()
[1] "/users/PZS0680/soottikkal/R/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu-library/3.6"
[2] "/usr/local/R/gnu/9.1/3.6.3/site/pkgs"
[3] "/usr/local/R/gnu/9.1/3.6.3/lib64/R/library"
Users can check the list of available packages as follows;
>installed.packages()
To install local R packages, use install.package() command. For example,
>install.packages("lattice")
For the first time local installation, it will give a warning as follows:
Installing package into ‘/usr/local/R/gnu/9.1/3.6.3/site/pkgs’
(as ‘lib’ is unspecified)
Warning in install.packages("lattice") :
'lib = "/usr/local/R/gnu/9.1/3.6.3/site/pkgs"' is not writable
Would you like to use a personal library instead? (yes/No/cancel)
Answer y , and it will create the directory and install the package there.
Installing Packages from GitHub
Users can install R packages directly from Github using devtools package as follows
>install.packages("devtools")
>devtools::install_github("author/package")
If you get errors related to the R XML package, see the Troubleshooting Issues section.
Installing Packages from Bioconductor
Users can install R packages directly from Bioconductor using BiocManager.
>install.packages("BiocManager")
>BiocManager::install(c("GenomicRanges", "Organism.dplyr"))
When installing R packages with external dependencies, users may need to import appropriate libraries into R. One of the frequently requested R packages is sf which needs geos, gdal and PROJ libraries (For more. We have a few versions of those packages installed and they can be loaded as modules. Another relativey common external dependency is gsl. To see what versions of modules are available, run the command module spider from the command line. For example, to see what version of gsl is available to load, run module spider gsl. The output will look something like this:
------------------------------------------------------------------------
gsl: gsl/2.7.1
------------------------------------------------------------------------
You will need to load all module(s) on any one of the lines below before the "gsl/2.7.1" module is available to load.
gcc/12.3.0
intel/2021.10.0
According to this output, we should run module load gcc/12.3.0 gsl/2.7.1 or module load intel/2021.10.0 gsl/2.7.1. You can also load modules directly from the R terminal in Rstudio:
> source(file.path(Sys.getenv("LMOD_PKG"), "init/R"))
> module("load", "geos/version")
For example, to load the module geos/3.12.0, you would run module("load", "geos/3.12.0"). You can check if an external pacakge is available
> module("avail", "geos")
When modules of external libs are not available, users can install those and link libraries to the R environment. Suppose you have locally installed gdal/3.3.1, and proj/9.2.1 at the path /users/<account-number>/<username>/local. Here is an example of how to install the sf package on Cardinal without modules.
# Update LD_LIBRARY_PATH to include user-installed libraries.
>old_ld_path <- Sys.getenv("LD_LIBRARY_PATH")
>Sys.setenv(LD_LIBRARY_PATH = paste(old_ld_path, "/users/<account-number>/<username>/local/gdal/3.3.1/lib", "/users/<account-number>/<username>/local/proj/9.2.1","/users/<account-number>/<username>/local/geos/3.9.1/lib",sep=":"))
>Sys.setenv("PKG_CONFIG_PATH"="/users/<account-number>/<username>/local/proj/9.2.1/lib/pkgconfig")
>Sys.setenv("GDAL_DATA"="/users/<account-number>/<username>/local/gdal/3.3.1/share/gdal")
>install.packages("sf", configure.args=c("--with-gdal-config=/users/<account-number>/<username>/local/gdal/3.3.1/bin/gdal-config","--with-proj-include=/users/<account-number>/<username>/local/proj/8.1.0/include","--with-proj-lib=/users/<account-number>/<username>/local/proj/9.2.1/lib"),INSTALL_opts="--no-test-load")
>dyn.load("/users/<account-number>/<username>/local/gdal/3.3.1/lib64/libgdal.so")
>dyn.load("/users/<account-number>/<username>/local/proj/9.2.1/lib64/libproj.so", local=FALSE)
>library(sf)
Please note that every time before loading sf package, you have to execute the dyn.load of both libraries listed above.
if you are using R for multiple projects, OSC recommendsrenv, an R dependency manager for R package management. Please see more information here.
The renv package helps you create reproducible environments for your R projects. Use renv to make your R projects more:
-
Isolated: Each project gets its own library of R packages, so you can feel free to upgrade and change package versions in one project without worrying about breaking your other projects.
-
Portable: Because renv captures the state of your R packages within a lockfile, you can more easily share and collaborate on projects with others, and ensure that everyone is working from a common base.
-
Reproducible: Use renv::snapshot() to save the state of your R library to the lockfile renv.lock. You can later use renv::restore() to restore your R library exactly as specified in the lockfile.
Users can install renv package as follows;
>install.packages("renv")
The core essence of the renv workflow is fairly simple:
-
After launching R, go to your project directory using R command setwd and initiate renv:
setwd("your/project/path")
renv::init()
This function forks the state of your default R libraries into a project-local library. A project-local .Rprofile is created (or amended), which is then used by new R sessions to automatically initialize renv and ensure the project-local library is used.
Work in your project as usual, installing and upgrading R packages as required as your project evolves.
-
Use renv::snapshot() to save the state of your project library. The project state will be serialized into a file called renv.lock under your project path.
-
Use renv::restore() to restore your project library from the state of your previously-created lockfile renv.lock.
In short: use renv::init() to initialize your project library, and use renv::snapshot() / renv::restore() to save and load the state of your library.
After your project has been initialized, you can work within the project as before, but without fear that installing or upgrading packages could affect other projects on your system.
Global Cache
One of renv’s primary features is the use of a global package cache, which is shared across all projects using renvWhen using renv the packages from various projects are installed to the global cache. The individual project library is instead formed as a directory of symlinks into the renv global package cache. Hence, while each renv project is isolated from other projects on your system, they can still re-use the same installed packages as required. By default, global Cache of renv is located ~/.local/share/renvUser can change the global cache location using RENV_PATHS_CACHE variable. Please see more information here.
Please note that renv does not load packages from site location (add-on packages installed by OSC) to the rsession. Users will have access to the base R packages only when using renv. All other packages required for the project should be installed by the user.
Version Control with renv
If you would like to version control your project, you can utilize git versioning of renv.lock file. First, initiate git for your project directory on a terminal
git init
Continue working on your R project by launching R, installing packages, saving snapshot using renv::snapshot()command. Please note that renv::snapshot() will only save packages that are used in the current project. To capture all packages within the active R libraries in the lockfile, please see the type option.
>renv::snapshot(type="simple")
If you’re using a version control system with your project, then as you call renv::snapshot() and later commit new lockfiles to your repository, you may find it necessary later to recover older versions of your lockfiles. renv provides the functions renv::history()to list previous revisions of your lockfile, and renv::revert() to recover these older lockfiles.
If you are using renvpackage for the first time, it is recommended that you check R startup files in your $HOME such as .Rprofile and .Renviron and remove any project-specific settings from these files. Please also make sure you do not have any project-specific settings in ~/.R/Makevars.
A Simple Example
First, you need to load the module for R and fire up R session
module load R/4.4.0
R
Then set the working directory and initiate renv
setwd("your/project/path")
renv::init()
Let's install a package called lattice, and save the snapshot to the renv.lock
renv::install("lattice")
renv::snapshot(type="simple")
The latticepackage will be installed in global cache of renv and symlink will be saved in renv under the project path.
Restore a Project
Use renv::restore() to restore a project's dependencies from a lockfile, as previously generated by snapshot(). Let's remove the lattice package.
renv::remove("lattice")
Now let's restore the project from the previously saved snapshot so that the lattice package is restored.
renv::restore()
library(lattice)
Collaborating with renv
When using renv, the packages used in your project will be recorded into a lockfile, renv.lock. Because renv.lock records the exact versions of R packages used within a project, if you share that file with your collaborators, they will be able to use renv::restore() to install exactly the same R packages as recorded in the lockfile. Please find more information here.
Please set the environment variables OMP_NUM_THREADS and MKL_NUM_THREADS to 1 in your job scripts. This adjustment helps avoid additional internal parallel processing by libraries such as OpenMP and MKL, which can otherwise conflict with parallelism set by R’s parallel processing packages.
R provides a number of methods for parallel processing of the code. Multiple cores and nodes available on OSC clusters can be effectively deployed to run many computations in R faster through parallelism.
Consider this example, where we use a function that will generate values sampled from a normal distribution and sum the vector of those results; every call to the function is a separate simulation.
myProc <- function(size=1000000) {
# Load a large vector
vec <- rnorm(size)
# Now sum the vec values
return(sum(vec))
}
Serial execution with loop
Let’s first create a serial version of R code to run myProc() 100x on Pitzer:
tick <- proc.time()
for(i in 1:100) {
myProc()
}
tock <- proc.time() - tick
tock
## user system elapsed
## 6.437 0.199 6.637
Here, we execute each trial sequentially, utilizing only one of our 28 processors on this machine. In order to apply parallelism, we need to create multiple tasks that can be dispatched to different cores. Using apply() family of R function, we can create multiple tasks. We can rewrite the above code to use apply(), which applies a function to each of the members of a list (in this case the trials we want to run):
tick <- proc.time()
result <- lapply(1:100, function(i) myProc())
tock <-proc.time() - tick
tock
## user system elapsed
## 6.346 0.152 6.498
parallel package
The parallellibrary can be used to dispatch tasks to different cores. The parallel::mclapply function can distributes the tasks to multiple processors.
library(parallel)
cores <- system("nproc", intern=TRUE)
tick <- proc.time()
result <- mclapply(1:100, function(i) myProc(), mc.cores=cores)
tock <- proc.time() - tick
tock
## user system elapsed
## 8.653 0.457 0.382
foreach package
The foreach package provides a looping construct for executing R code repeatedly. It uses the sequential %do% operator to indicate an expression to run.
library(foreach)
tick <- proc.time()
result <-foreach(i=1:100) %do% {
myProc()
}
tock <- proc.time() - tick
tock
## user system elapsed
## 6.420 0.018 6.439
doParallel package
foreach supports a parallelizable operator %dopar% from the doParallel package. This allows each iteration through the loop to use different cores.
library(doParallel, quiet = TRUE)
library(foreach)
cl <- makeCluster(28)
registerDoParallel(cl)
tick <- proc.time()
result <- foreach(i=1:100, .combine=c) %dopar% {
myProc()
}
tock <- proc.time() - tick
tock
invisible(stopCluster(cl))
detachDoParallel()
## user system elapsed
## 0.085 0.013 0.446
Rmpi package
Rmpi package allows to parallelize R code across multiple nodes. Rmpi provides an interface necessary to use MPI for parallel computing using R. This allows each iteration through the loop to use different cores on different nodes. Rmpijobs cannot be run with RStudio at OSC currently, instead users can submit Rmpi jobs through terminal App. R uses openmpi as MPI interface therefore users would need to load openmpi module before installing or using Rmpi. Rmpi is installed at central location for R versions prior to 4.2.1. If it is not availbe, users can install it as follows
Rmpi Installation
# Get source code of desired version of RMpi
wget https://cran.r-project.org/src/contrib/Rmpi_0.7-2.tar.gz
# Load modules
ml openmpi/5.0.2 gcc/12.3.0 R/4.4.0
# Install RMpi
R CMD INSTALL --configure-vars="CPPFLAGS=-I$MPI_HOME/include LDFLAGS='-L$MPI_HOME/lib'" --configure-args="--with-Rmpi-include=$MPI_HOME/include --with-Rmpi-libpath=$MPI_HOME/lib --with-Rmpi-type=OPENMPI" Rmpi_0.7-2.tar.gz
# Test loading
library(Rmpi)
Please make sure that $MPI_HOME is defined after loading openmpi module. Newer versions of openmpi module has $OPENMPI_HOME instead of $MPI_HOME. So you would need to replace $MPI_HOME with $OPENMPI_HOME for those versions of openmpi.
Above example code can be rewritten to utilize multiple nodes with Rmpias follows;
library(Rmpi)
library(snow)
workers <- as.numeric(Sys.getenv(c("PBS_NP")))-1
cl <- makeCluster(workers, type="MPI") # MPI tasks to use
clusterExport(cl, list('myProc'))
tick <- proc.time()
result <- clusterApply(cl, 1:100, function(i) myProc())
write.table(result, file = "foo.csv", sep = ",")
tock <- proc.time() - tick
tock
Batch script for job submission is as follows;
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --time=10:00
#SBATCH --nodes=2 --ntasks-per-node=28
#SBATCH --account=<project-account>
#SBATCH --export=ALL,OMP_NUM_THREADS=1,MKL_NUM_THREADS=1
module reset
module load openmpi/5.0.2 gcc/12.3.0 R/4.4.0
# parallel R: submit job with one MPI master
mpirun -np 1 R --slave < Rmpi.R
pbdMPI package
pbdMPI is an improved version of the Rmpi package that provides efficient interface to MPI by utilizing S4 classes and methods with a focus on Single Program/Multiple Data ('SPMD') parallel programming style, which is intended for batch parallel execution. This means that all processes (ranks) run the same code independently. pbdMPI also uses OpenMPI as an MPI interface.
Installation of pbdMPI
Users can download latest version of pbdMPI from CRAN https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/pbdMPI/index.html and install it as follows:
wget https://cran.r-project.org/src/contrib/pbdMPI_0.5-3.tar.gz
ml gcc/12.3.0
ml R/4.4.0
ml openmpi/5.0.2
R CMD INSTALL pbdMPI_0.5-3.tar.gz
Examples
Example of a matrix calculation using pbdMPI:
# Load the pbdMPI package
library(pbdMPI, quietly = TRUE)
# Initialize MPI environment
init()
# Each rank creates 2 matrices with random data
matrix_size = 5
set.seed(100 + comm.rank())
A <- matrix(rnorm(matrix_size^2), nrow = matrix_size)
B <- matrix(rnorm(matrix_size^2), nrow = matrix_size)
# Multiply the matrices
C <- A %*% B
# Gather all C matrices to rank 0
gathered_C <- gather(C, rank.dest = 0)
# On rank 0, compute the global sum of all
if (comm.rank() == 0) {
global_sum <- Reduce("+", gathered_C)
cat("Global sum of all C matrices:\n")
print(global_sum)
}
finalize()
An example batch job submission script is as follows:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --time=00:10:00
#SBATCH --nodes=2 --ntasks-per-node=4
#SBATCH --account=<project-account>
#SBATCH --export=ALL,OMP_NUM_THREADS=1,MKL_NUM_THREADS=1
module reset
module load gcc/12.3.0 R/4.4.0 openmpi/5.0.2
mpirun Rscript pbdMPI-script.R
Note that one copy of this script will be run for each node, so the total number of tasks will affect the total number of matrices operations computed. In this example with 8 total tasks, 16 total matrices will be created (2 per task).
Here are additional resources that demonstrate how to use pbdMPI:
https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/pbdMPI/pbdMPI.pdf
http://hpcf-files.umbc.edu/research/papers/pbdRtara2013.pdf
Paralell R jobs can be monitored in Grafana by visiting the link outputted from the command job-dashboard-link.py <jobid>.
The R package, batchtools provides a parallel implementation of Map for high-performance computing systems managed by schedulers Slurm on OSC system. Please find more info here https://github.com/mllg/batchtools.
Users would need two files slurm.tmpl and .batch.conf.R
Slurm.tmpl is provided below. Please change "your project_ID".
#!/bin/bash -l
## Job Resource Interface Definition
## ntasks [integer(1)]: Number of required tasks,
## Set larger than 1 if you want to further parallelize
## with MPI within your job.
## ncpus [integer(1)]: Number of required cpus per task,
## Set larger than 1 if you want to further parallelize
## with multicore/parallel within each task.
## walltime [integer(1)]: Walltime for this job, in seconds.
## Must be at least 60 seconds.
## memory [integer(1)]: Memory in megabytes for each cpu.
## Must be at least 100 (when I tried lower values my
## jobs did not start at all).
## Default resources can be set in your .batchtools.conf.R by defining the variable
## 'default.resources' as a named list.
<%
# relative paths are not handled well by Slurm
log.file = fs::path_expand(log.file)
-%>
#SBATCH --job-name=<%= job.name %>
#SBATCH --output=<%= log.file %>
#SBATCH --error=<%= log.file %>
#SBATCH --time=<%= ceiling(resources$walltime / 60) %>
#SBATCH --ntasks=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=<%= resources$ncpus %>
#SBATCH --mem-per-cpu=<%= resources$memory %>
#SBATCH --account=your_project_id
<%= if (!is.null(resources$partition)) sprintf(paste0("#SBATCH --partition='", resources$partition, "'")) %>
<%= if (array.jobs) sprintf("#SBATCH --array=1-%i", nrow(jobs)) else "" %>
## Initialize work environment like
## source /etc/profile
## module add ...
module add R/4.0.2-gnu9.1
## Export value of DEBUGME environemnt var to slave
export DEBUGME=<%= Sys.getenv("DEBUGME") %>
<%= sprintf("export OMP_NUM_THREADS=%i", resources$omp.threads) -%>
<%= sprintf("export OPENBLAS_NUM_THREADS=%i", resources$blas.threads) -%>
<%= sprintf("export MKL_NUM_THREADS=%i", resources$blas.threads) -%>
## Run R:
## we merge R output with stdout from SLURM, which gets then logged via --output option
Rscript -e 'batchtools::doJobCollection("<%= uri %>")'
.batch.conf.R is provided below.
cluster.functions = makeClusterFunctionsSlurm(template="path/to/slurm.tmpl")
A test example is provided below. Assuming the current working directory has both slurm.tmpl and .batch.conf.R files.
ml gcc/12.3.0 R/4.4.0
R
>install.packages("batchtools")
>library(batchtools)
>myFct <- function(x) {
result <- cbind(iris[x, 1:4,],
Node=system("hostname", intern=TRUE),
Rversion=paste(R.Version()[6:7], collapse="."))}
>reg <- makeRegistry(file.dir="myregdir", conf.file=".batchtools.conf.R")
>Njobs <- 1:4 # Define number of jobs (here 4)
>ids <- batchMap(fun=myFct, x=Njobs)
>done <- submitJobs(ids, reg=reg, resources=list( walltime=60, ntasks=1, ncpus=1, memory=1024))
>waitForJobs()
>getStatus() # Summarize job
Profiling R code helps to optimize the code by identifying bottlenecks and improve its performance. There are a number of tools that can be used to profile R code.
Grafana:
OSC jobs can be monitored for CPU and memory usage using grafana. If your job is in running status, you can get grafana metrics as follows. After log in to OSC OnDemand, select Jobs from the top tabs, then select Active Jobs and then Job that you are interested to profile. You will see grafana metrics at the bottom of the page and you can click on detailed metrics to access more information about your job at grafana.
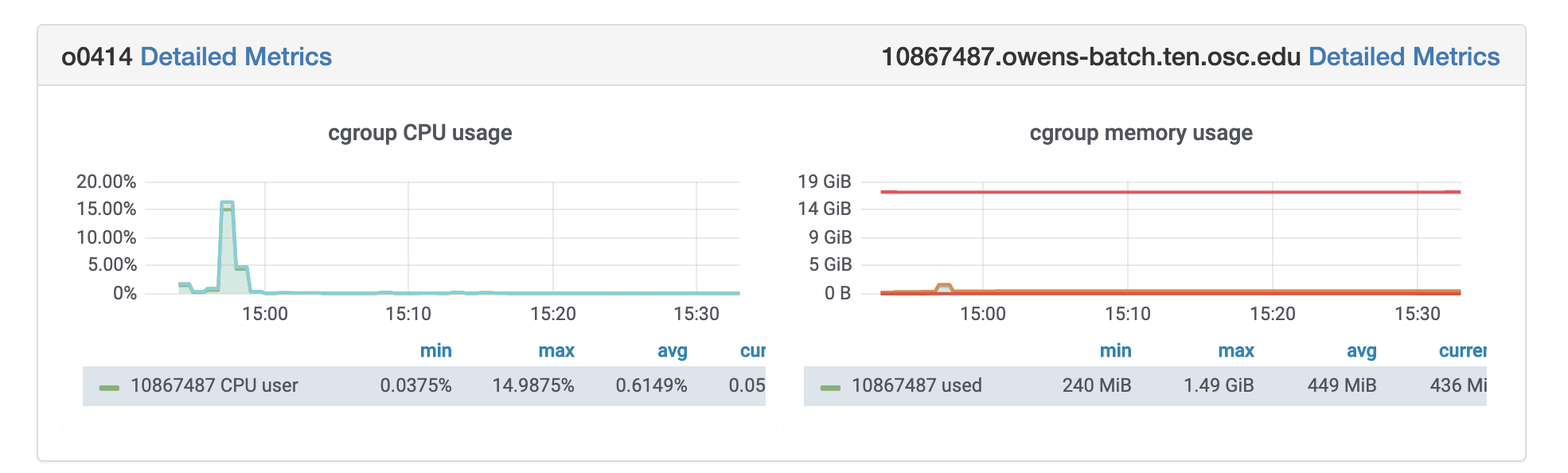
Rprof:
R’s built-in tool,Rprof function can be used to profile R expressions and the summaryRprof function to summarize the result. More information can be found here.
Here is an example of profiling R code with Rprofe for data analysis on Faithful data.
Rprof("Rprof-out.prof",memory.profiling=TRUE, line.profiling=TRUE)
data(faithful)
summary(faithful)
plot(faithful)
Rprof(NULL)
To analyze profiled data, runsummaryRprof on Rprof-out.prof
summaryRprof("Rprof-out.prof")
You can read more about summaryRprofhere.
Profvis:
It provides an interactive graphical interface for visualizing data from Rprof.
library(profvis)
profvis({
data(faithful)
summary(faithful)
plot(faithful)
},prof_output="profvis-out.prof")
If you are running the R code on Rstudio, it will automatically open up the visualization for the profiled data. More info can be found here.
OSC provides an isolated and custom R environment for each classroom project that requires Rstudio. More information can be found here.
Further Reading
Check .bashrc
If you're encountering difficulties launching the RStudio App on-demand or errors with installing packages, the first step is to review your ~/.bashrc file. Check for custom configurations and any conda/python related lines. Consider commenting out these configurations and attempting to launch the app or re-install the package.
R session taking too long to initialize
If your R session is taking too long to initialize, it might be due to issues from a previous session. First, make sure no Rstudio jobs are running. Then restore R to a fresh session by removing the previous state stored at
~/.local/share/rstudio (~/.rstudio for <R/4.1)
mv ~/.local/share/rstudio ~/.local/share/rstudio.backup
Common Problem Packages
Several packages are known to have problems installing.
XML
For R XML, the libxml2 library must be preloaded. This is sometimes also needed for packages that depend on the XML package, such as rtracklayer.
> Sys.setenv("LD_PRELOAD"="/lib64/libxml2.so")
> dyn.load("/lib64/libxml2.so")
> install.packages("XML")
sf
For sf: proj and gdal modules must be loaded. Follow the instructions in the R packages with external dependencies section to see which versions of these modules are available and load them. You must also call dyn.load on their libraries. To find out the correct path, run the command module show module/version. For example, run module show proj/9.2.1, if this is the version available. The output should include a line that looks like this:
> setenv("PROJ_HOME","/apps/spack/0.21/pitzer/linux-rhel9-skylake/proj/gcc/12.3.0/9.2.1-buhooyr")
The dyn.load command is the path here concatenated with /lib/libproj.so. Follow the same steps for gdal. Here is full example of the install steps on Pitzer:
> source(file.path(Sys.getenv("LMOD_PKG"), "init/R"))
> module("load", "proj/9.2.1")
> module("load", "gdal/3.7.3")
> dyn.load("/apps/spack/0.21/pitzer/linux-rhel9-skylake/proj/gcc/12.3.0/9.2.1-buhooyr/lib64/libproj.so")
> dyn.load("/apps/spack/0.21/pitzer/linux-rhel9-skylake/gdal/gcc/12.3.0/3.7.3-wmnbnyd/lib64/libgdal.so")
> install.packages("sf")
> library("sf")
Now you can install other packages that depend on sf normally.
This is an example of the stars package installation, which has a dependency of sf package.
>install.packages("stars")
>library(stars)
rJava
For rJava, please run the following command before attempting installation:
Last updated 9/25/25
Pitzer:
> Sys.setenv(LDFLAGS = "-L/apps/spack/0.21/pitzer/linux-rhel9-skylake/libiconv/gcc/12.3.0/1.17-bcgrlj2/lib)
Ascend:
> Sys.setenv(LDFLAGS = "-L/apps/spack/0.21/ascend/linux-rhel9-zen2/libiconv/gcc/12.3.0/1.17-wifr2il/lib)
Cardinal
> Sys.setenv(LDFLAGS = "-L/apps/spack/0.21/cardinal/linux-rhel9-sapphirerapids/libiconv/gcc/12.3.0/1.17-fxsid3a/lib
Further Reading
See Also