Computer-aided engineering (CAE) has supported the advancement of technology and manufacturing throughout the world. While extensive CAE software suites meet most of the market’s needs, some software providers cater to clients with more specialized engineering requirements.
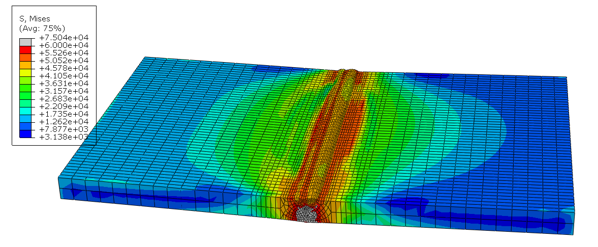
QustomApps LLC is a small software company in Ponder, Texas, that provides two specialized software programs, WoundSIM and QustomWeld, used in precision weld simulation and composite pressure vessel modeling.
The founder of QustomApps, Mike Shubert, began his career at Hibbitt, Karlsson & Sorensen, Inc., a CAE vendor now known as Dassault Systèmes Simulia Corp. The company develops Abaqus, a popular CAE suite used in a wide range of engineering applications.
After 28 years working with Abaqus, Shubert retired from Dassault Systèmes Simulia to follow his passion for precision engineering software by creating his company, QustomApps. Taking his knowledge of Abaqus, he stripped down the expansive program to create WoundSIM and QustomWeld.
“There are certain engineering applications that are so specialized that Abaqus cannot tailor their software directly to them,” Shubert said. “What QustomApps does is customize Abaqus for this set of narrower applications, making it much easier to use.”
QustomWeld is used to simulate welds varying in scale, from large nuclear reactors all the way down to the electronics within smart phones. Simulating these welds with high precision is computationally intensive and requires the use of high performance computing (HPC). Because of this, some of Shubert’s clients need to run QustomApps software on the Linux operating system due to its ease of use and popularity within HPC.
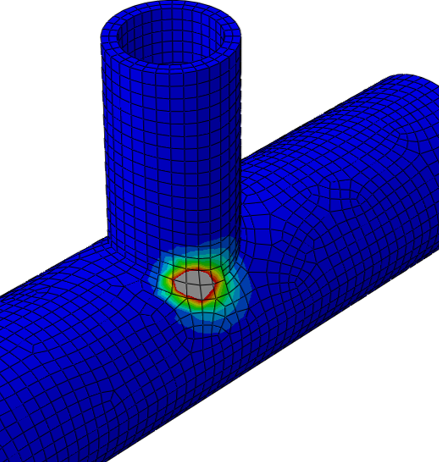
Adapting QustomApps software to run on Linux proved to be more of a challenge than Shubert expected. He first attempted to build a Linux machine to write and test Linux versions of his applications. Due to the complexity of the operating system, running his own machine quickly became infeasible.
“I was fighting with that machine for two years; I can’t tell you how much money and time I wasted on it,” Shubert said. “The luckiest thing that happened to me was when I got connected to the Ohio Supercomputer Center.”
Introduced to OSC through one of his clients, Shubert applied for an account and began compiling his code within OSC’s Linux-based machines. This allowed Shubert to continuously develop and update his software without the added struggles of maintaining his own Linux machine.
OSC was especially helpful to QustomApps because of its backlog of Abaqus versions. One of Shubert’s customers runs a legacy version of the software that is no longer available for download but is still accessible on OSC’s machines.
“Without OSC I would never be able to help many of my clients,” Shubert said. “I was able to help extend the reach of an Ohio company, Dante Solutions, out to the global welding industry. They now have customers all the way in Korea using their software.”
Shubert plans to use OSC’s resources indefinitely, updating his software multiple times per year. OSC has become an essential tool within Shubert’s process, eliminating a major roadblock within his work.
“OSC has been a lifesaver for me,” Shubert said. “What used to be a major problem is now just a trivial part of my business.”
By Kiah Easton
About OSC: The Ohio Supercomputer Center (OSC) addresses the rising computational demands of academic and industrial research communities by providing a robust shared infrastructure and proven expertise in advanced modeling, simulation and analysis. OSC empowers scientists with the services essential to making extraordinary discoveries and innovations, partners with businesses and industry to leverage computational science as a competitive force in the global knowledge economy and leads efforts to equip the workforce with the key technology skills required for 21st century jobs.