Architecture Simulations
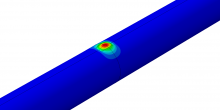
Rendering models is a key part of the modern architectural design process. Brendan Ho, a professor in the College of Architecture and Environmental Design at Kent State University, helps students analyze the spaces they live and work in. Rendering has been an essential component in his studio Encapsulated Episodes, co-taught with Director Ivan Bernal.