Electrical Double Layers
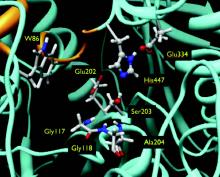
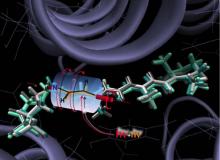
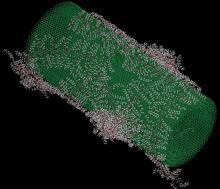
Many biological molecules and common surfaces carry an electrical charge. For example, DNA has a strong negative charge, and so does an amorphous form of silicon dioxide known as silica, the material most people recognize as “glass.” A charged molecule or surface, along with the electrically compensating layer of ions in the adjacent solution, is known as the electrical double layer (EDL).