MATLAB is a technical computing environment for high-performance numeric computation and visualization. MATLAB integrates numerical analysis, matrix computation, signal processing, and graphics in an easy-to-use environment where problems and solutions are expressed just as they are written mathematically--without traditional programming.
Availability and Restrictions
Versions
MATLAB is available on OSC Clusters. The versions currently available at OSC are:
| Version | Pitzer | Ascend | Cardinal |
|---|---|---|---|
| r2024a | X | X | X* |
| r2024b | X |
You can use module spider matlab to view available modules for a given machine. Feel free to contact OSC Help if you need other versions for your work.
Matlab is also available through Jupyter, please see the Running MATLAB on Jupyter section for more information.
Access: Academic Users Only (non-commercial, non-government)
Academic users can use Matlab at OSC. All users must be added to the license server before using MATLAB. Please contact OSC Help to be granted access or for any license related questions.
Publisher/Vendor/Repository and License Type
MathWorks, Commercial (University site license)
Toolboxes and Features
OSC's current licenses support the following MATLAB toolboxes and features (please contact OSC Help for license-specific questions):
MATLAB Simulink 5G Toolbox AUTOSAR Blockset Aerospace Blockset Aerospace Toolbox Antenna Toolbox Audio Toolbox Automated Driving Toolbox Bioinformatics Toolbox Communications Toolbox Computer Vision Toolbox Control System Toolbox Curve Fitting Toolbox DDS Blockset DSP System Toolbox Data Acquisition Toolbox Database Toolbox Datafeed Toolbox Deep Learning HDL Toolbox Deep Learning Toolbox Econometrics Toolbox Embedded Coder Filter Design HDL Coder Financial Instruments Toolbox Financial Toolbox Fixed-Point Designer Fuzzy Logic Toolbox GPU Coder Global Optimization Toolbox HDL Coder HDL Verifier Image Acquisition Toolbox Image Processing Toolbox Instrument Control Toolbox LTE Toolbox Lidar Toolbox MATLAB Coder MATLAB Compiler SDK MATLAB Compiler MATLAB Report Generator Mapping Toolbox Mixed-Signal Blockset Model Predictive Control Toolbox Model-Based Calibration Toolbox Motor Control Blockset Navigation Toolbox OPC Toolbox Optimization Toolbox Parallel Computing Toolbox Partial Differential Equation Toolbox Phased Array System Toolbox Powertrain Blockset Predictive Maintenance Toolbox RF Blockset RF PCB Toolbox RF Toolbox ROS Toolbox Radar Toolbox Reinforcement Learning Toolbox Risk Management Toolbox Robotics System Toolbox Robust Control Toolbox Satellite Communications Toolbox Sensor Fusion and Tracking Toolbox SerDes Toolbox Signal Integrity Toolbox Signal Processing Toolbox SimBiology SimEvents Simscape Driveline Simscape Electrical Simscape Fluids Simscape Multibody Simscape Simulink 3D Animation Simulink Check Simulink Code Inspector Simulink Coder Simulink Compiler Simulink Control Design Simulink Coverage Simulink Design Optimization Simulink Design Verifier Simulink Desktop Real-Time Simulink PLC Coder Simulink Real-Time Simulink Report Generator Simulink Requirements Simulink Test SoC Blockset Spreadsheet Link Stateflow Statistics and Machine Learning Toolbox Symbolic Math Toolbox System Composer System Identification Toolbox Text Analytics Toolbox UAV Toolbox Vehicle Dynamics Blockset Vehicle Network Toolbox Vision HDL Toolbox WLAN Toolbox Wavelet Toolbox Wireless HDL Toolbox
See this page if you need to install additional toolbox by yourself.
Usage
Usage on Pitzer
Set-up
module load matlab.Running MATLAB
The following command will start an interactive, command line version of MATLAB:
matlab -nodisplayIf you are able to use X-11 forwarding and have enabled it in your SSH client software preferences, you can run MATLAB using the GUI by typing the command
matlab. For more information about the matlab command usage, type matlab –h for a complete list of command line options.
The commands listed above will run MATLAB on the login node you are connected to. As the login node is a shared resource, running scripts that require significant computational resources will impact the usability of the cluster for others. As such, you should not use interactive MATLAB sessions on the login node for any significant computation. If your MATLAB script requires significant time, CPU power, or memory, you should run your code via the batch system.
Batch Usage
When you log into pitzer.osc.edu you are actually logged into a Linux box referred to as the login node. To gain access to the multiple processors in the computing environment, you must submit your job to the batch system for execution. Batch jobs can request multiple nodes/cores and compute time up to the limits of the OSC systems. Refer to Queues and Reservations and Batch Limit Rules for more info.
Interactive Batch Session
For an interactive batch session using the command line version of MATLAB, one can run the following command:sinteractive -A <project-account> -N 1 -n 40 -t 00:20:00
which requests one whole node with 40 cores ( -N 1 -n 40), for a walltime of 20 minutes ( -t 00:20:00 ). Here you can run MATLAB interactively by loading the MATLAB module and running MATLAB with the options of your choice as described above. You may adjust the numbers per your need.
Additional Topics
MATLAB Parallel Functions and Tools
MATLAB now supports Parallel Computing Toolbox. The Parallel Computing Toolbox lets you solve computationally and data-intensive programs using multiple cores and GPUs. Built in MATLAB functions and tools allow for easy parallelization of MATLAB applications. Programs can be run both interactively or as batch jobs.
Please refer to the official MATLAB documentation for more information on the Parallel Computing Toolbox
Sections:
Creating Parallel Pools
You can parallelize by requesting a certain number of workers and then work can be offloaded onto those pool of workers. For local computations, the number of workers you can requests relates to the number of cores available.
To start up a pool you can run:
p = gcp
p is the pool object which can be used to check information on the worker pool.
By default gcp creates a pool of workers equal to the number of cores on the job.
Note:
- It may takes a couple of seconds to a minute to start up a pool.
- You cannot run multiple parallel pools at the same time on a single job.
To delete the current pool if one exists run:
delete(gcp('nocreate')
After the program is done running the pool will still remain active. MATLAB only deletes the pool after the default 30 minutes. So if you want to end a pool you must manually delete it, let MATLAB timeout the pool. or terminate the job. If you make changes to the code interactively it is recommended you delete the pool and spin up a new pool of workers.
See Matlab documentation for more information on worker pools here
Parpool and Batch
Parallel jobs can also be submitted by a Matlab script, as is demonstrated below in the Submitting Single-Node Parallel MATLAB Jobs and Submitting Multi-Node Parallel MATLAB Jobs sections. The 2 main ways of doing so is through parpool and batch.
First, before using parpool or batch, you must get a handle to the profile cluster. To do this use the parcluster function.
% creates cluster profile object for the specified cluster profile
c = parcluster("Cluster_Profile");
% creates a cluster object to your current job
c = parcluster("local");
See the Submitting Multi-Node Parallel MATLAB Jobs section below for more information on how to create a cluster profile.
Creating the object with a cluster profile will result in a new job to be submitted when launching parpool or batch. Make sure the appropriate arguments are set in the cluster profile. Creating the object with the 'local' parameter will not result in a new job to be launched when executing parpool or batch. Instead the workers will be allocated to the cores in your current job.
Once you have you a profile object created, you can now launch parallel jobs.
To launch a parpool parallel job, simply run:
p = parpool(c, 40); % c: is the cluster profile object initialized using parcluster % 40: because we want 40 workers
Important Note: You can only run one parpool job at a time. You need to make sure the parent job which launched the parpool job has a long enough wall time to accommodate the new job otherwise the parpool job will get terminated when the parent job ends.
To launch a batch job:
job1 = batch(c, @function, 1, {"arg1", "arg2"}, "Pool", 40); % launch batch job of 40 workers
% c: is the cluster profile object initialized using parcluster
wait(job1); % wait for job to finish
X = fetchOutputs(job1); %retrieve the output data from job
%job detail can be accessed by the job1 object including its status.
Here we launched a batch job to exectute @function. @function will be run on a parallel pool of 40 workers.
Since batch does not block up your matlab program, you wan use the wait function to wait for your batch job(s) to finish before proceeding. The fetchOutputs function can be used to retrieve the outputs of the batch job.
The notable difference between parpool and batch is that you can run multiple batch jobs at a time and their duration is not tied to the parent job (the parent job can finish executing and the batch jobs will continue executing unlike parpool).
please refer to the official MATLAB documentation for more details: parcluster parpool batch
Parfor
To parallelize a for-loop you can use a parfor-loop.
A parfor-loop will run the different iterations of the loop in parallel by assigning the iterations to the workers in the pool. If multiple jobs are assigned to a worker then those jobs will be competed in serial by the worker. It is important to carefully assess and make good judgment calls on how many workers you want to request for the job.
To utilize a parfor-loop simply replace the for in a standard for-loop with parfor.
%converting a standard for loop to a parfor looks as such:
for i=1:10
%loop code
end
%replace the for with parfor
parfor i=1:10
%loop code
end
Important note: parfor may complete the iterations out of order, so it is important that the iterations are not order dependent.
A parfor-loop is run synchronously, thus the MATLAB process is halted until all tasks for the workers are settled.
Important Limitations:
- Cannot nest parfors inside of one another: This is because workers cannot start or access further parallel pools.
- parfor-loops and for-loops can be nested inside one another (it is often a judgment call on whether it is better to nest a parfor inside a for-loop or vice versa).
%valid
for i=1:10
parfor j=1:10
%code
end
end
%invalid: will throw error
parfor i=1:10
parfor j=1:10
%code
end
end
- Cannot have loop elements dependent on other iterations
- Since, there is not guaranteed order of completion of iterations in a parfor-loop and workers cannot communicate with each other, each loop iteration must be independent.
A = ones(1,100);
parfor i = 1:100
A(i) = A(i-1) + 1; %invalid iteration entry as the current iteration is dependent on the previous iteration
end
- step size must be 1
parfor i = 0:0.1:1 %invalid because step side is not 1
%code
end
To learn more about par-for loops see the official matlab parfor documentation
Parfeval
Another way to run loops in parallel in MATLAB is to use parfeval loops. When using parfeval to run functions in the background it creates an object called a future for each function and adds the future object to a poll queue.
First, initialize a futures object vector with the number of expected futures. Preallocation of the futures vector is not required, but is highly recommended to increase efficiency: f(1:num_futures) = parallel.FevalFuture;
For each job, you can fill the futures vector with an instance of the future. Filling the vector allows you to get access to the futures later. f(index) = parfeval(@my_function, numOutputs, input1, input2);
@my_functionis the pointer to the function I want to runnumOutputsis the integer represented number of returned outputs you need frommy_function. Note: this does not need to match the actual number for outputs the function returns.input1, input2, ...is the parameter list formy_function
%example code f(1:10) = parallel.FevalFuture; for i = 1:10 f(i) = parfeval(@my_function, 1, 2); end
when a future is created, it is added to a queue. Then the workers will takes futures from the queue to begin to evaluate them.
you can use the state property of a future to find out whether it is queued, running, or finished: f(1).State
you can manually cancel a future by running: cancel(f(1));
you can block off MATLAB until a certain future complete by using: wait(f(4));
when a future is finished you can check its error message is one was thrown by: f(1).Error.message
You can cancel all running and/or queued futures by (p is the parallel pool object):
cancel(p.FevalQueue.QueuedFutures); cancel(p.FevalQueue.RunningFutures);
Processing worker outputs as they complete
One of the biggest strengths of parfeval is its ability to run futures asynchronously (runs in the background without blocking the Matlab program). This allows you to fetch results from the futures as they get completed.
p = gcp; %luanch parallel pool with number of workers equal to availble cores
f(1:10) = parallel.FevalFuture; % initalize futures vector
for k = 1:10
f(k) = parfeval(@rand, 1, 1000, 1); % lanch 10 futures which will run in background on parallel pool
end
results = cell(1,10); % create a results vector
for k = 1:10
[completedK, value] = fetchNext(f); % fetch the next worker that finished and print its results
results{completedK} = value;
fprintf("got result with index: %d, largest element in vector is %f. \n", completedK, max(results{completedK}));
end
In this example above, as each @rand future gets completed by the workers, the fetchNext retrieves the returned data.
MATLAB also provides functions such at afterEach and afterAll to process the outputs as workers complete futures.
Please refer to the official MATLAB documentation for more information on parfeval: parfeval and parfeval parallel pooling
Spmd
spmd stands for Single Program Multiple Data. The spmd block can be used to execute multiple blocks of data across multiple workers. Here is a simple example:
delete(gcp('nocreate')); %delete a parallel pool if one is already spun up
p = parpool(2); %create a pool of 2 workers
spmd
fprintf("worker %d says hello world", spmdIndex); %have each worker print statement
end
%end of code
%output Worker 1: worker 1 says hello world Worker 2: worker 2 says hello world %end of output
The spmdIndex variable can be used to access the index of each worker. spmd also allows for communication between workers via sending and receiving data. Additionally, data can be received by the MATLAB client from the workers. For more information on spmd and its functionality vist the Official MATLAB documentation
Submitting Single-Node Parallel MATLAB Jobs
When parallelizing on a single node, you can generate and run a parallel pool on the same node as the current job or interactive secession.
Here is an example MATLAB script of submitting a parallel job to a single node:
p = parcluster('local');
% open parallel pool of 8 workers on the cluster node
parpool(p, 8);
spmd
% assign each worker a print function
fprintf("Worker %d says Hello", spmdIndex);
end
delete(gcp); % close the parallel pool
exit
Since we will only be using a single node, we will use the 'local' cluster profile. This will create a profile object p which will be the cluster profile of the job the command was run in. We also set the pool size be less than or equal to the number of cores on our compute node; In this case we will used 8. See cluster specifications to see the maximum number of cores on a single node for each cluster.
Now lets save this MATLAB script as "wokrer_hello.m" and write a Slurm batch script to submit and execute it as a job. "worker_hello.slurm" slurm script:
#!/bin/bash #SBATCH --job-name=worker_hello # job name #SBATCH --cpus-per-task=8 # 8 cores #SBATCH --output=worker_hello.log # set output file #SBATCH --time=00:10:00 # 10 minutes wall time # load Matlab module module load matlab/r2023a cd $SLURM_SUBMIT_DIR #run matlab script matlab -nodisplay -r worker_hello
In this script first we set a MATLAB module to the module path, in this example its MATLAB/r2023a. Then we make a call to execute the "worker_hello.m" MATLAB script. The -nodisplay flag is to prevent matlab from attempting to launch a GUI. In this script we requested 8 cores since our MATLAB script uses 8 workers. When performing single node parallelizations be mindful of the max number of cores each node has on the different clusters.
Then the job was submitted using sbatch -A <project-account> worker_hello.slurm through the command line.
The output was then generated into the "worker_hello.log" file:
< M A T L A B (R) >
Copyright 1984-2023 The MathWorks, Inc.
R2023a Update 2 (9.14.0.2254940) 64-bit (glnxa64)
April 17, 2023
To get started, type doc.
For product information, visit www.mathworks.com.
Starting parallel pool (parpool) using the 'Processes' profile ...
Connected to parallel pool with 8 workers.
Worker 1:
Worker 1 says Hello
Worker 2:
Worker 2 says Hello
Worker 3:
Worker 3 says Hello
Worker 4:
Worker 4 says Hello
Worker 5:
Worker 5 says Hello
Worker 6:
Worker 6 says Hello
Worker 7:
Worker 7 says Hello
Worker 8:
Worker 8 says Hello
Parallel pool using the 'Processes' profile is shutting down.
As we see a total of 8 workers were created and each printed their message in parallel.
Create Cluster Profile
Before we can parallelize matlab across multiple nodes we need to create a cluster profile. In the profile we can specify any arguments and adjust the settings of submitting jobs through MATLAB.
If you are running matlab r2019b and newer you can run configCluster to configure matlab with the profile of the cluster your job is running on:
configCluster % configer matlab with profile c = parcluster; % get a handle to cluster profile % set any additional properties c.AdditionalProperties.WallTime = '00:10:00'; % set wall time to 10 mintues c.AdditionalProperties.AccountName = 'PZS1234' % set account name c.saveProfile % locally save the profile
AccountName and WallTime and make sure to save the profile.
If the above method does not work, or you prefer to to use the GUI, then you can configure a cluster profile from the GUI. You must be running MATLAB r2023a and newer versions to be able to search for OSC's clusters.
1. First we need to launch a Matlab GUI through onDemand. See onDemand for more details.
2. Next within the MATLAB GUI, navigate to HOME->Environment->Parallel->Discover Clusters:

3. Then check the "On your network" box. Then click Next.

4. If you started the Matlab GUI though onDemand then you should see the cluster of the session listed as such (I started mine through Pitzer so Pitzer is listed):
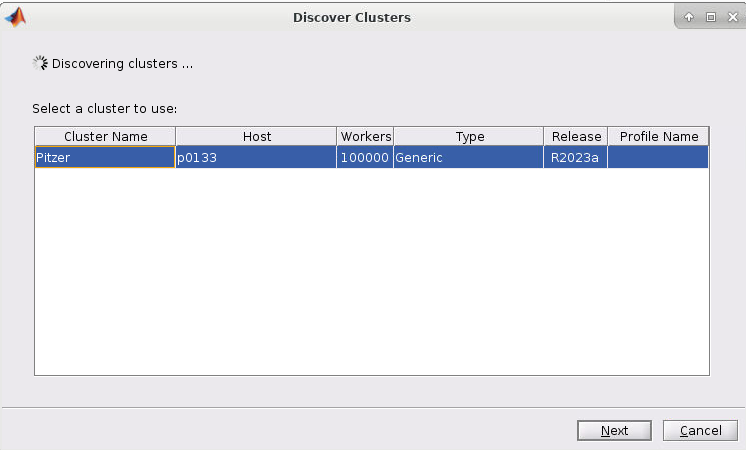
5. Now select the cluster and click Next. You should now have a screen like this:
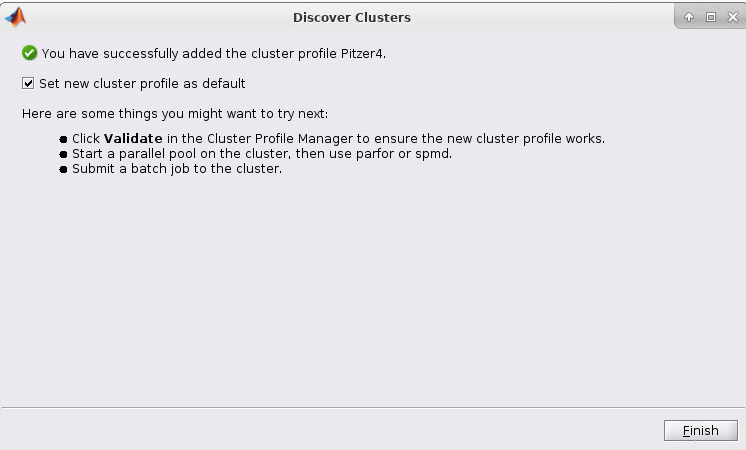
6. Now check the "Set new cluster profile as default" box and then click Finish
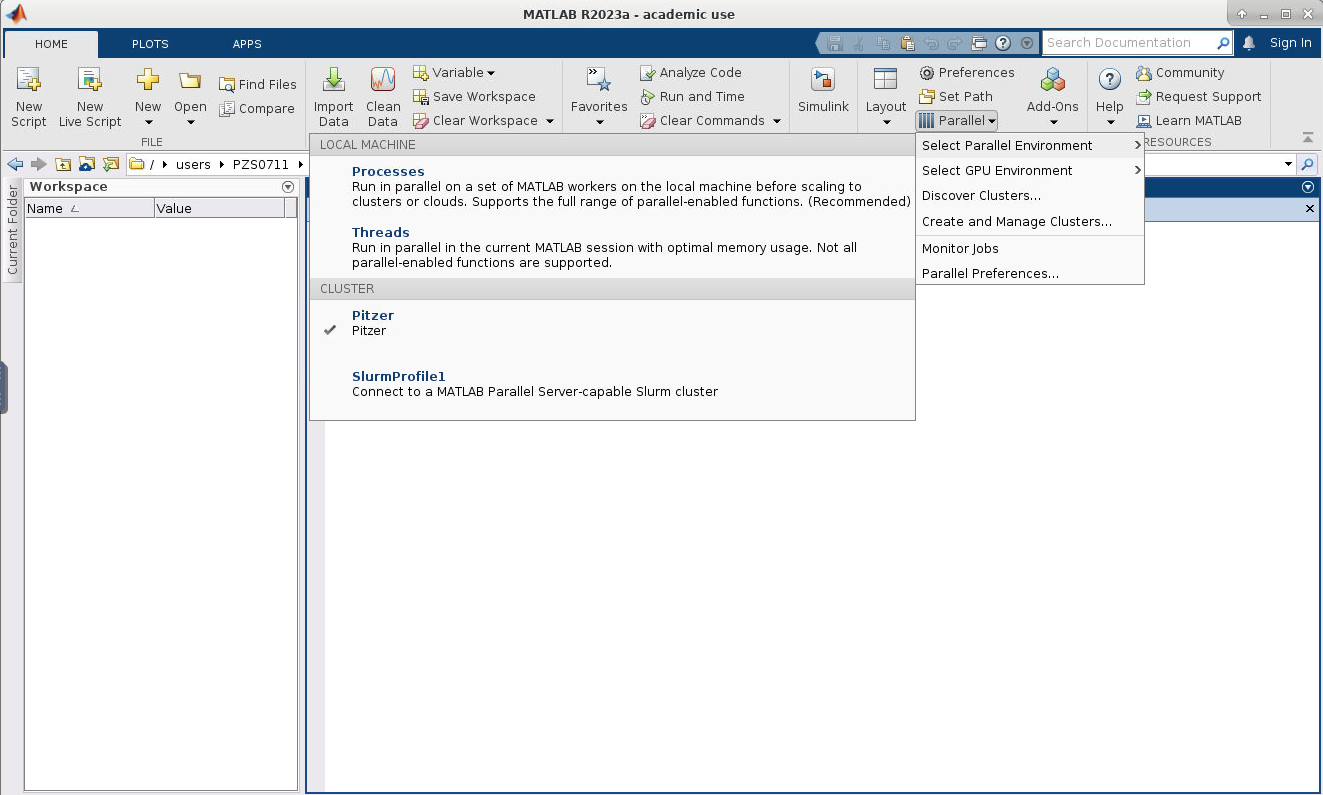
7. Now if you click on HOME->Environment->Parallel->Select Parallel Environment you will be presented with a list of profiles available which you can toggle between. Your new profile that was just created should be listed.
8. Now we need to edit the cluster profile to suit the needs of the job we want to submit. Go to HOME->Environment->Parallel->Create and Manage Clusters. Select the cluster profile you want to edit and then click edit. Most settings can be left as default but the following must be set: the AccountName and WallTime under the SCHEDULER PLUGIN must be set to your account name:
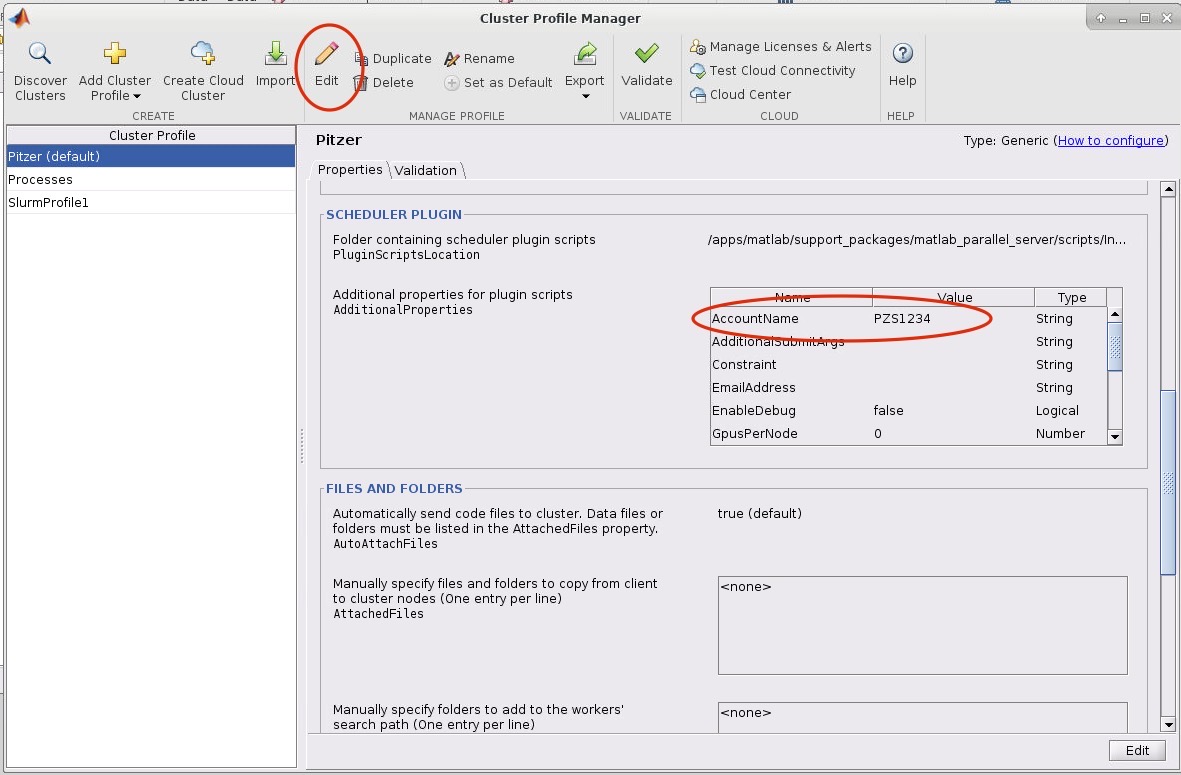
If you want MATLAB to submit jobs with slurm parameters other than the default you may edit them in this menu.
AccountName and WallTime Validating Profile
If you run into any issues using your cluster profile you may want to validate your profile. Validating is not required, but may help debug any profile related issues.
To validate a profile:
- Within the MATLAB GUI, navigate to HOME->Environment->Parallel->Create and Manage Clusters:
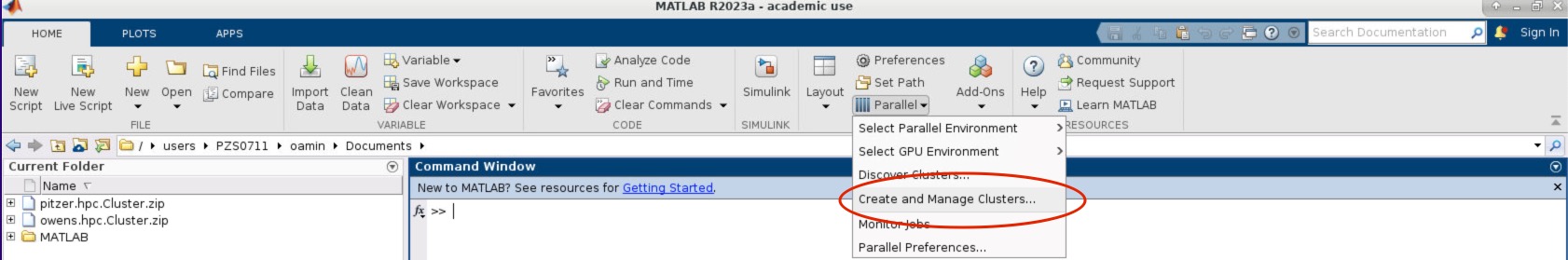
- Select the profile you want to validate on the left side of the menu. Then select the Validation tab next to the Properties tab. Now in the Number of worker to use: box specifiy the number of cores you are using to run the OnDemand MATLAB GUI on. If you leave the box blank, then it will run the tests with more workers then cores available to your matlab session which will result in a failed validation.
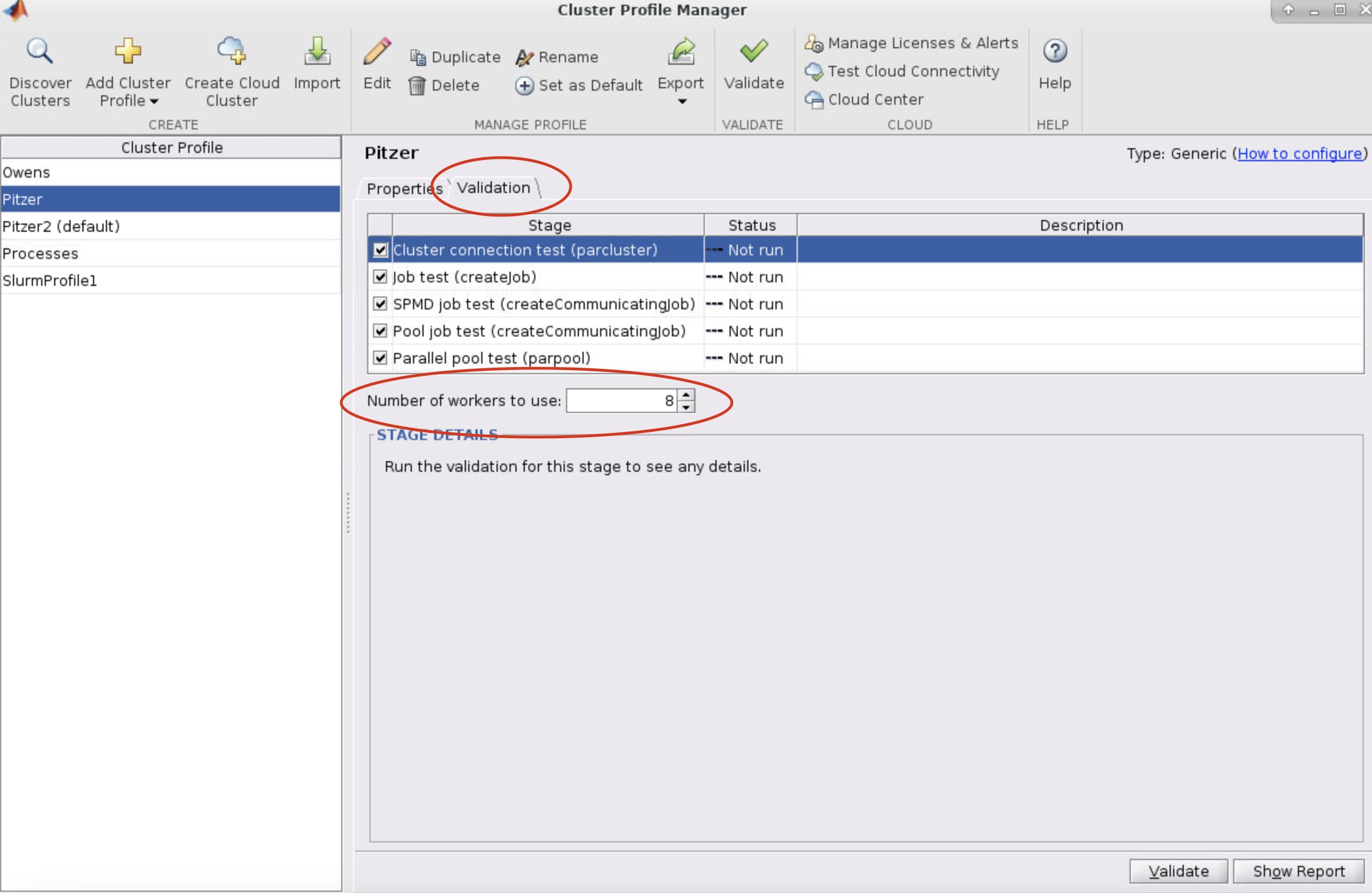
-
Next, click validate in the bottom right or top of the menu
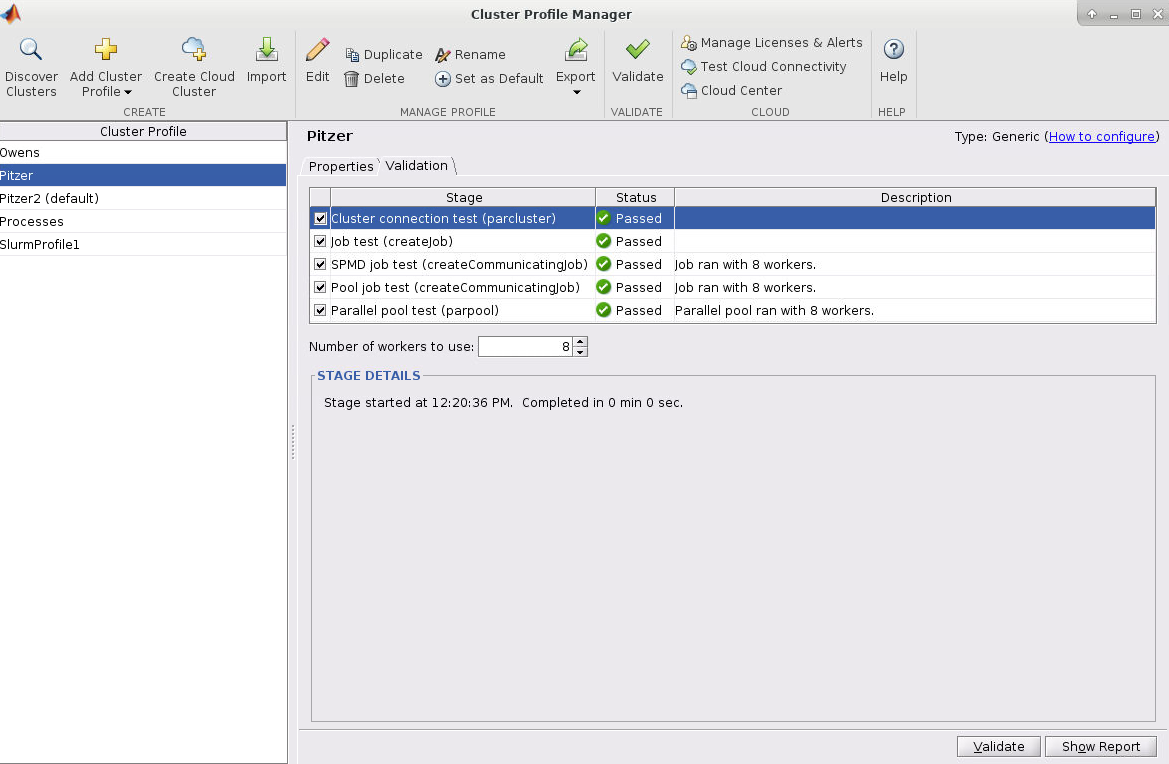
AccountName and WallTime are both set in the cluster profile before validating! Make sure the number of worker used for validation is less than or equal to the number of cores available to the MATLAB session!Submitting Multi-Node Parallel MATLAB Jobs
Before Submitting multi-node parallel jobs you must create a cluster profile. See Create Cluster Profile section above.
Now let's create a submit a multi-node parallel MATLAB job. Here is a matlab script:
configCluster % configer matlab with profile
p = parcluster; % get a handle to cluster profile
% set any additional properties
p.AdditionalProperties.WallTime = '00:10:00'; % set wall time to 10 mintues
p.AdditionalProperties.AccountName = 'PZS1234' % set account name
p.saveProfile % locally save the profile
% if profile created using the "Discover Clusters" from the GUI then you can simply run: p = parcluster('Pitzer'); instead of the above code.
% open parallel pool of 80 workers
parpool(p, 80); % you must specify the number of workers you want
spmd
fprintf("Worker %d says Hello", spmdIndex);
end
delete(gcp); % close the parallel pool
exit
In this example we opened a cluster profile called 'Pitzer'. This profile name should be the same as the cluster profile created above. We then launched another job using the parpool function with 80 workers onto the Pitzer cluster with the default settings (wall-time was set to 1 minutes instead of the default 1 hour). Since 80 workers is over the maximum number of cores per node, the Pitzer profile created using the steps above will automatically request 2 nodes for the job to accomodate the workers.
This script was saved in a file called "hello_multi_node.m".
Now a slurm script was created as follows:
#!/bin/bash #SBATCH --job-name=hello_multi_node # job name #SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1 # 1 cores #SBATCH --output=hello_multi_node.log # set output file #SBATCH --time=00:10:00 # 10 minutes wall time # load Matlab module module load matlab/r2023a cd $SLURM_SUBMIT_DIR #run matlab script matlab -nodisplay -r hello_multi_node
This job was allocated only 1 core. This is because the "hello_multi_node.m" will launch another job on the Pitzer cluster when calling parpool to exectute the parallel workers. Since the main entry matlab program does not need multiple nodes, we only allocated 1.
Then the job was submitted using sbatch -A <project-account> hello_multi_node.slurm through the command line.
The output was then generated into the "hello_multi_node.log" file:
< M A T L A B (R) >
Copyright 1984-2023 The MathWorks, Inc.
R2023a Update 2 (9.14.0.2254940) 64-bit (glnxa64)
April 17, 2023
To get started, type doc.
For product information, visit www.mathworks.com.
Starting parallel pool (parpool) using the 'Pitzer' profile ...
additionalSubmitArgs =
'--ntasks=80 --cpus-per-task=1 --ntasks-per-node=40 -N 2 --ntasks-per-core=1 -A PZS0711 --mem-per-cpu=4gb -t 00:01:00'
Connected to parallel pool with 80 workers.
Worker 1:
Worker 1 says hello
Worker 2:
Worker 2 says hello
Worker 3:
Worker 3 says hello
Worker 4:
Worker 4 says hello
Worker 5:
Worker 5 says hello
.
.
.
Worker 80:
Worker 80 says hello
Notice by the additionalSubmitArgs = line another job was launched with 2 nodes with 40 cores on each node. It is in this new job that the workers completed their tasks.
In this example we used parpool to launch a new parallel job, but batch can also be used. See MATLAB Parallel Functions and Tools for more information on the batch function
You can modify the properties of a cluster profile through code aswell through the c.AdditionalProperties attribute. This is helpful if you want to submit multiple batch jobs through a single Matlab program with different submit arguments.
c = parcluster('Pitzer'); % get cluster object
c.AdditionalProperties.WallTime = "00:15:00"; % sets the wall time to the c cluster object. Does not change the 'Pitzer' profile itself, only the local object.
c.saveProfile; % saves to the central 'Pitzer' profile.
Multithreading
Multithreading allows some functions in MATLAB to distribute the work load between cores of the node that your job is running on. By default, all of the current versions of MATLAB available on the OSC clusters have multithreading enabled.
The system will run as many threads as there are cores on the nodes requested.
Multithreading increases the speed of some linear algebra routines, but if you would like to disable multithreading you may include the option " -singleCompThread" when running MATLAB. An example is given below:
#!/bin/bash #SBATCH --job-name disable_multithreading #SBATCH --time=00:10:00 #SBATCH --nodes=1 --ntasks-per-node=40 #SBATCH --account=<project-account> module load matlab matlab -singleCompThread -nodisplay -nodesktop < hello.m # end of example file
Using GPU in MATLAB
A GPU can be utilized for MATLAB. You can acquire a GPU for the job by
#SBATCH --gpus-per-node=1
for Pitzer. For more detail, please read here.
You can check the GPU assigned to you using:
gpuDeviceCount # show how many GPUs you have gpuDevice # show the details of the GPU
To utilize a GPU, you will need to transfer the data from a standard CPU array to a GPU array. gpuArrays are a data structure which is stored on the GPU. Make sure the GPU has enough memory to hold this data. Even if the gpuArray fits in the GPU memory, make sure that any temporary arrays and data generated will also be able to fit on the GPU.
To create a GPU array:
X = [1,2,3]; %create a standard array G = gpuArray(X); %transfer array over to gpu
To check if data is stored on the GPU run:
isgpuarray(G); %returns true or false
To transfer the GPU data back onto the host memory use:
Y = gather(G);
Note:
- To reduce overhead time, limit the amount of data transfers between the host memory and GPU memory. For instance, many MATLAB functions allow you to create data directly on the GPU by specify the "gpuArray" parameter:
gpu_matrix = rand(N, N, "gpuArray"); - Gathering data from gpuArrays can be costly in terms of time and thus it is generally not necessary to gather the data unless you need to store it or the data needs processing to through non-gpu compatible functions.
When you have data in a GPU Array there are many built-in MATLAB functions which can run on the data. See list on the MATLAB website for a full list of compatible functions.
For more information about GPU programming for MATLAB, please read GPU Computing from Mathworks.
Running Concurrent Jobs
Concurrent jobs on OSC clusters
When you run multiple jobs concurrently, each job will try to access your preference files at the same time. It may create a race condition issue and may cause a negative impact on the system and the failure of your jobs. In order to avoid this issue, please add the following in your job script:
export MATLAB_PREFDIR=$TMPDIR
It will reset the preference directory to the local temporary directory, $TMPDIR. If you wish to start your Matlab job with the preference files you already have, add the following before you change MATLAB_PREFDIR.
cp -a ~/.matlab/{matlab version}/* $TMPDIR/
If you use matlab/r2020a, your matlab version is "R2020a".
Running MATLAB in Jupyter
MATLAB can be run on Jupyter Notebooks! First you will need to create a kernel, and then it will be available on Cardinal through a Jupyter session
Creating the Kernel
Run the following script, substituting {matlab version} with the version of MATLAB available on Cardinal you would like to run code for in Jupyter. You can have kernels of different versions as long as they are supported on Cardinal
~support/scripts/jupyter-matlab/create_jupyter_matlab_kernel {matlab version}
If you use matlab/r2024b your version is r2024b
You should receive a message like
## Creating the Jupyter MATLAB kernel in ~/.local/share/jupyter/kernels/jupyter_matlab_kernel_{matlab version};
A kernel directory will have been created at ~/.local/share/jupyter/kernels/jupyter_matlab_kernel_{matlab version}. To delete a kernel, you can remove that directory
rm -rf ~/.local/share/jupyter/kernels/jupyter_matlab_kernel_{matlab version}
Running Matlab in Jupyter
First, select the MATLAB kernel now available in Jupyter on OnDemand. It will be named "MATLAB Kernel {matlab version}"
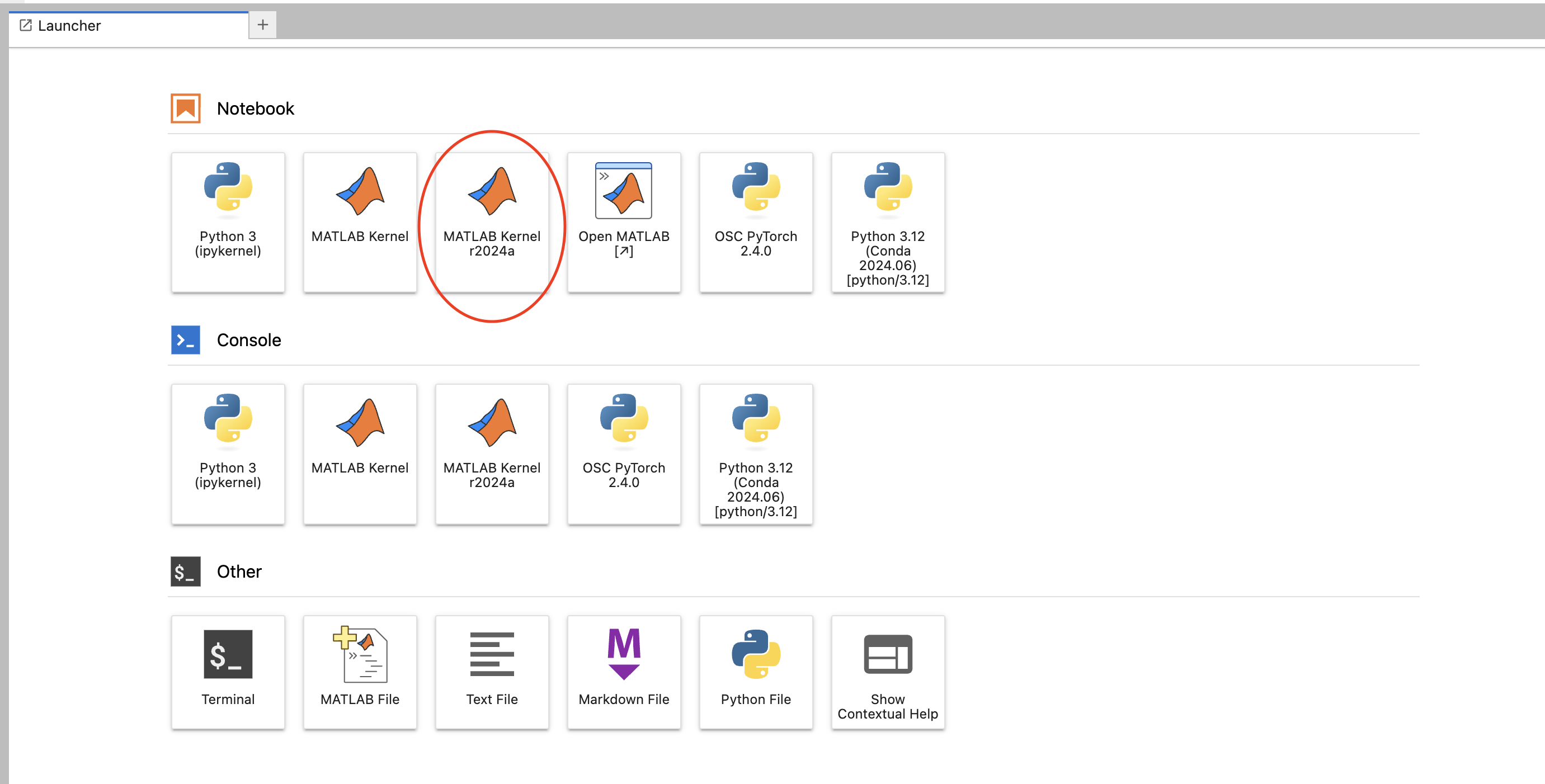
Enter in any MATLAB code in the box. When you first run the code MATLAB will take time to start up, then you are ready to go!
![]()
References
- Official PDF documentation can be obtained from the MathWorks Website.
- Using MatLab's Parallel Server for multi-core and multi-node jobs.